Understanding Borderline ECG: What You Need To Know
This ambiguous classification can leave patients feeling uncertain about their heart health. An ECG, a non-invasive test that records the electrical activity of the heart, is a critical diagnostic tool for identifying potential heart conditions. However, when the results are labeled as "borderline," it indicates that some aspects of the readings are slightly outside the normal range but not severe enough to warrant an immediate diagnosis. Understanding what this means is essential for patients and their families, as it can guide further medical evaluation and decision-making. A borderline ECG can arise from a variety of factors, ranging from benign causes like stress or dehydration to more serious underlying conditions such as arrhythmias or structural heart abnormalities. While the term itself might sound alarming, it’s important to note that a borderline result does not always indicate a serious problem. In many cases, lifestyle factors, temporary physiological changes, or even technical issues during the test can contribute to borderline findings. This is why healthcare providers often recommend repeat testing or additional diagnostic procedures to confirm the initial results. By understanding the nuances of a borderline ECG, patients can better navigate their healthcare journey and make informed decisions about their well-being. The implications of a borderline ECG can vary widely depending on the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and risk factors. For some, it may be a harmless anomaly that resolves on its own, while for others, it could signal the need for closer monitoring or intervention. Regardless of the outcome, early detection and awareness are key to managing potential heart-related issues. In this article, we will delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, and diagnostic processes associated with borderline ECG results, helping you gain a clearer understanding of what this finding means for your health.
Table of Contents
- What Does a Borderline ECG Indicate?
- How Can You Differentiate Between Normal and Abnormal ECG Findings?
- What Are the Common Causes of a Borderline ECG?
- Symptoms and Signs Associated with Borderline ECG Results
- Diagnosis and Follow-Up Testing for Borderline ECG
- Is a Borderline ECG a Sign of Heart Disease?
- Treatment Options and Lifestyle Changes for Borderline ECG
- Frequently Asked Questions About Borderline ECG
What Does a Borderline ECG Indicate?
A borderline ECG is not a definitive diagnosis but rather a signal that some aspects of the heart’s electrical activity are slightly outside the normal range.
This could include variations in heart rate, rhythm, or electrical conduction patterns that don’t align perfectly with standard benchmarks. These findings are often flagged by automated ECG machines and reviewed by cardiologists to determine their clinical significance. For instance, a slightly prolonged QT interval or minor ST-segment changes might be labeled as borderline, prompting further investigation to rule out underlying conditions.
Read also:Dawn Wells Measurements A Complete Guide To Her Life And Career
It’s crucial to understand that a borderline ECG is not synonymous with heart disease. Many factors can influence ECG readings, including age, body composition, and even the position of electrodes during the test. For example, athletes often exhibit ECG patterns that differ from the general population due to their high level of cardiovascular fitness. Similarly, individuals with electrolyte imbalances, such as low potassium or magnesium levels, may present with borderline findings that resolve once the imbalance is corrected. These examples highlight the importance of context when interpreting ECG results.
Healthcare providers typically approach a borderline ECG with caution, as it can sometimes indicate early signs of conditions like atrial fibrillation, ventricular hypertrophy, or ischemic heart disease. However, it’s equally possible that the findings are transient or benign. To determine the next steps, doctors may consider the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and risk factors such as family history of heart disease, smoking, or hypertension. This comprehensive evaluation helps ensure that patients receive appropriate care without unnecessary alarm or intervention.
How Can You Differentiate Between Normal and Abnormal ECG Findings?
Understanding the difference between normal and abnormal ECG findings is essential for interpreting borderline ECG results accurately.
An ECG records the timing and strength of electrical signals as the heart beats, producing a graph with distinct waves, intervals, and segments. A normal ECG shows a consistent pattern: the P wave represents atrial depolarization, the QRS complex reflects ventricular depolarization, and the T wave indicates ventricular repolarization. Any deviation from these patterns may be flagged as abnormal, but not all deviations are cause for concern.
For example, a normal heart rate typically falls between 60 and 100 beats per minute (bpm), while bradycardia (below 60 bpm) or tachycardia (above 100 bpm) might raise red flags. However, trained athletes often have a resting heart rate below 60 bpm due to their conditioned cardiovascular systems, which is considered normal for them. Similarly, a slight variation in the PR interval (the time between atrial and ventricular contraction) might be classified as borderline rather than abnormal if the patient is asymptomatic and has no underlying heart conditions.
Key Indicators of Abnormal ECG Findings
To differentiate between normal and abnormal findings, healthcare providers look for specific markers:
Read also:Discovering The Impact Of Fox Lisa Boothe A Comprehensive Guide
- ST-Segment Changes: Elevation or depression of the ST segment can indicate myocardial ischemia or infarction.
- QT Interval Prolongation: A prolonged QT interval may increase the risk of arrhythmias, such as torsades de pointes.
- Q Waves: Deep or wide Q waves can suggest a prior heart attack.
- Irregular Rhythms: Atrial fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia are examples of abnormal rhythms that require immediate attention.
Why Context Matters in ECG Interpretation
Context is critical when evaluating ECG results. For instance, a borderline finding in a young, healthy individual with no symptoms may be less concerning than the same result in an older adult with a history of heart disease. Additionally, external factors such as caffeine consumption, stress, or recent physical activity can temporarily alter ECG readings. By considering the patient’s overall health, symptoms, and lifestyle, healthcare providers can better determine whether a borderline ECG requires further investigation or if it’s a harmless anomaly.
What Are the Common Causes of a Borderline ECG?
A borderline ECG can arise from a variety of factors, ranging from benign and temporary conditions to more serious underlying health issues.
Understanding these causes is essential for both patients and healthcare providers to determine the appropriate course of action. Below, we explore some of the most common reasons behind borderline ECG findings, categorized into physiological, lifestyle-related, and pathological factors.
Physiological Causes
Physiological factors refer to natural variations in the body that can influence ECG results without indicating a pathological condition. These include:
- Age: As people age, changes in heart structure and electrical conduction can lead to borderline findings. For example, older adults may exhibit a slightly prolonged PR interval or minor ST-segment changes.
- Body Composition: Obesity or a lean physique can affect how electrical signals travel through the chest, potentially leading to borderline readings.
- Athletic Conditioning: Athletes often have slower resting heart rates (bradycardia) and larger heart chambers, which can result in ECG patterns that differ from those of non-athletes.
Lifestyle-Related Factors
Lifestyle choices and habits can also contribute to borderline ECG results. These factors are often reversible with appropriate changes:
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress can increase heart rate and cause transient changes in ECG readings.
- Dehydration: Low fluid levels can affect electrolyte balance, leading to abnormal electrical activity in the heart.
- Caffeine and Stimulants: Consuming excessive amounts of caffeine or using stimulants like nicotine can temporarily alter heart rhythm and ECG patterns.
Pathological Causes
In some cases, a borderline ECG may indicate an underlying medical condition that requires further evaluation. These pathological causes include:
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Abnormal levels of potassium, magnesium, or calcium can disrupt the heart’s electrical activity.
- Hypertension: Long-term high blood pressure can lead to left ventricular hypertrophy, which may appear as borderline findings on an ECG.
- Heart Disease: Conditions such as coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, or arrhythmias can produce borderline ECG results.
Symptoms and Signs Associated with Borderline ECG Results
While a borderline ECG may not always be accompanied by noticeable symptoms, certain signs and symptoms can provide valuable context for healthcare providers.
Recognizing these indicators is crucial for determining whether further investigation is necessary. Below, we explore the most common symptoms and signs associated with borderline ECG findings, along with their potential implications.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Patients with a borderline ECG may experience a range of symptoms, although these are not always present. Some of the most frequently reported symptoms include:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: While not always indicative of a serious issue, chest pain should never be ignored, as it can signal underlying heart problems.
- Palpitations: A sensation of rapid, fluttering, or irregular heartbeats can be linked to arrhythmias or other heart conditions.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity, may suggest reduced heart function or underlying cardiovascular issues.
Less Common but Important Signs
In addition to the more common symptoms, certain less frequent signs may also warrant attention:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness, even after adequate rest, can indicate that the heart is not pumping efficiently.
- Dizziness or Fainting: These symptoms may point to issues with heart rhythm or blood flow to the brain.
- Swelling in the Legs or Ankles: Fluid retention can be a sign of heart failure or other cardiovascular conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many borderline ECG findings are benign, certain symptoms should prompt immediate medical evaluation. These include severe chest pain, fainting episodes, or palpitations accompanied by shortness of breath. Additionally, individuals with risk factors such as a family history of heart disease, diabetes, or high blood pressure should be particularly vigilant about monitoring their symptoms and discussing them with their healthcare provider.
Diagnosis and Follow-Up Testing for Borderline ECG
When a borderline ECG result is identified, the next step is to conduct a thorough evaluation to determine its clinical significance.
This process often involves a combination of diagnostic tests and follow-up evaluations to rule out underlying conditions and provide clarity. Below, we explore the various diagnostic tools and procedures commonly used in conjunction with a borderline ECG, as well as the importance of follow-up testing.
Diagnostic Tools for Further Evaluation
Several diagnostic tools can help healthcare providers better understand the implications of a borderline ECG. These include:
- Holter Monitor: A portable device worn for 24 to 48 hours to record continuous ECG data, helping to identify intermittent arrhythmias or other abnormalities.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart that provides detailed images of its structure and function, useful for detecting structural abnormalities like hypertrophy or valve issues.
- Stress Test: Also known as an exercise ECG
Discover The Magic Of Famous Scorpios: Unveiling Their Secrets
Who Is Jameliz Benitez Smith? Discovering The Inspiring Journey Of A Rising Star
Who Is Paul Hauser? A Comprehensive Guide To His Life And Achievements
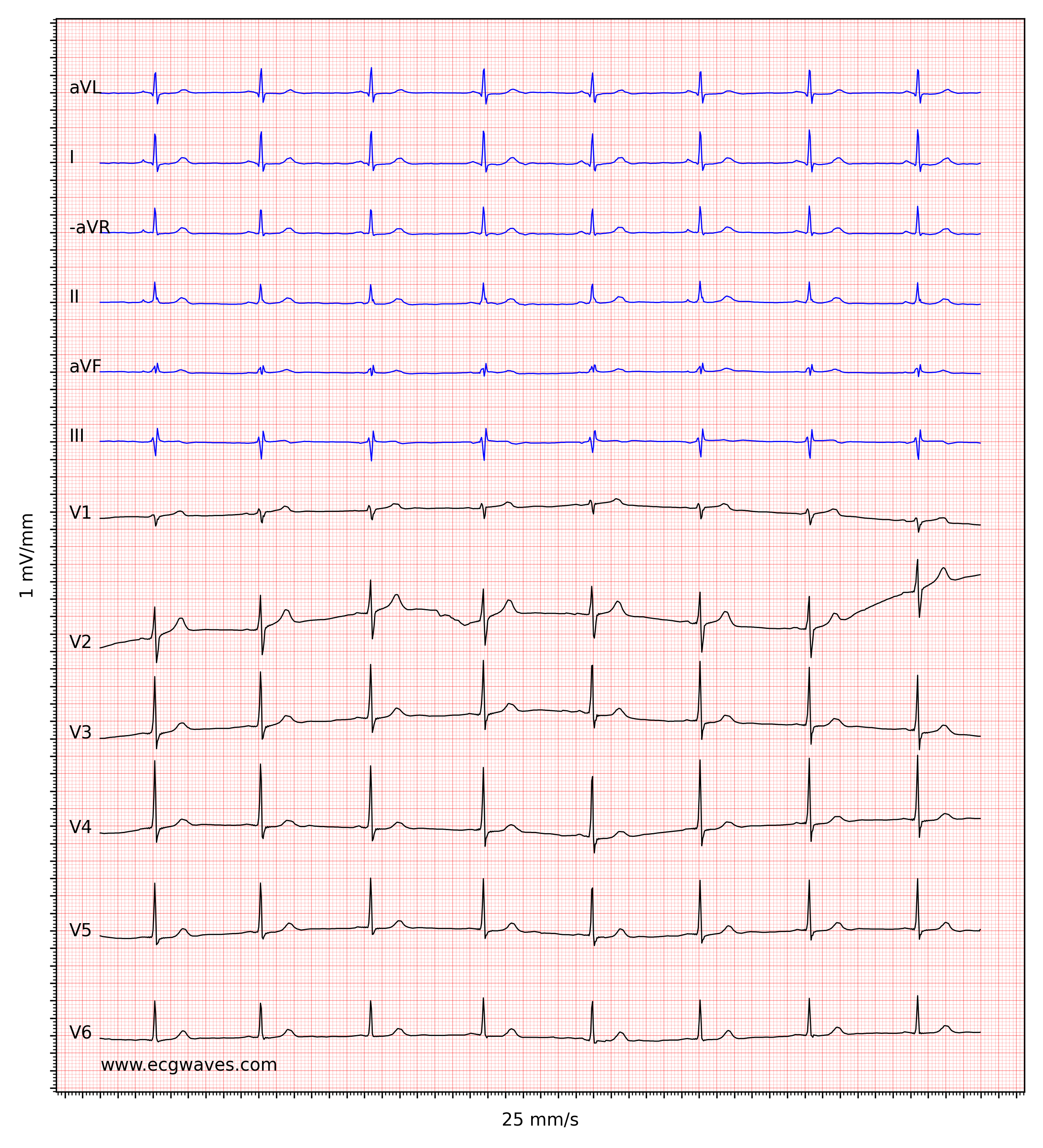
Borderline Rhythm On Ecg Hot Sale www.jkuat.ac.ke

Borderline Rhythm On Ecg Hot Sale www.jkuat.ac.ke